Heartwarming Info About Can DC Voltage Be Stepped Up
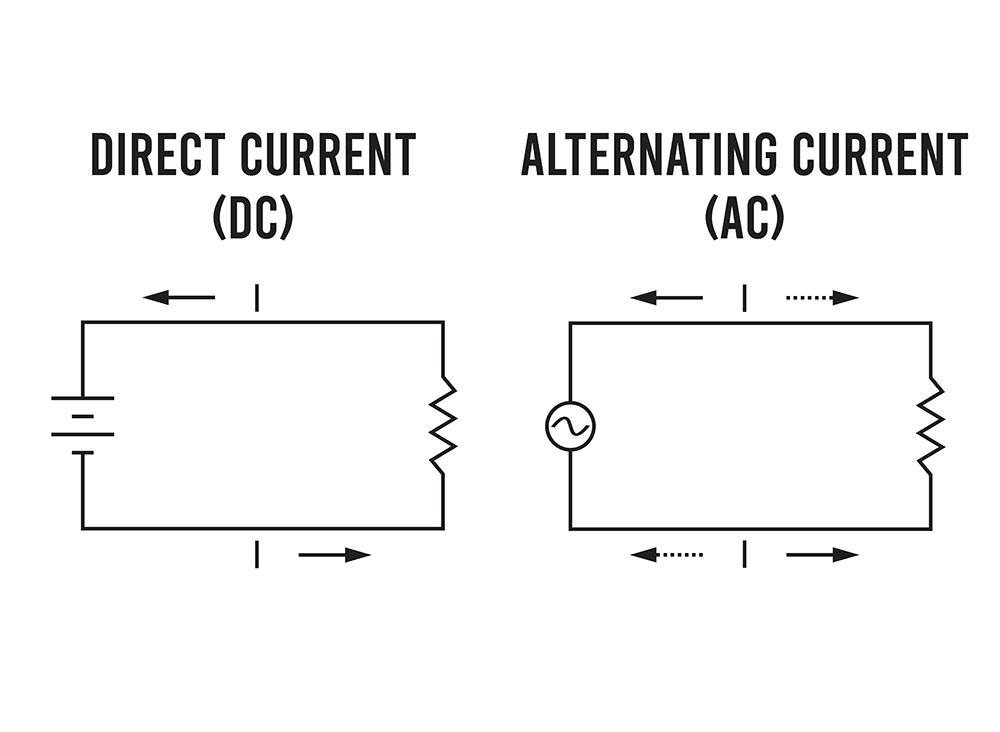
Stepping Up DC Voltage
1. The Short Answer — Yes, But How?
So, you're wondering if you can boost that Direct Current (DC) voltage, huh? The kind you get from batteries or solar panels? Well, the good news is: Yes, absolutely! It's not magic; it's just clever engineering. Think of it like this: you've got a little stream of water (DC voltage), and you want to make it a bigger, more powerful stream. You need some equipment to do that, of course, it just cannot happen on it's own.
The important thing to remember is that stepping up voltage doesn't create energy from nothing. Energy must be conserved. This means that if you increase the voltage, you'll usually decrease the current (amps). It's like trading width for height — the total amount of "water" (power) stays roughly the same, minus some inevitable losses due to inefficiencies.
Why would you even want to increase DC voltage? Loads of reasons! Maybe you have a bunch of solar panels putting out a low voltage, and you need to get it up to a level that can charge a battery bank efficiently. Or perhaps you're building a cool DIY gadget that requires a higher voltage than your power source provides. Whatever the reason, boosting DC voltage is a common requirement in many electronic applications.
One more thing to bear in mind: dealing with electricity, even low-voltage DC, requires caution. Always double-check your wiring, use appropriate components, and if you're not comfortable with electronics, seek advice from someone who is. Safety first, always!

Can DC Voltage Be Steppedup To Electric Motor Requirements In An
How it's Done
2. The Heart of the Operation
Okay, so we know it's possible to step up DC voltage, but how exactly do we do it? The answer lies in a nifty piece of circuitry called a DC-DC converter. These converters are like little transformers for DC power. They take a lower voltage DC input and convert it to a higher voltage DC output. It's kind of like an electronic pump that pushes the voltage higher.
There are several different types of DC-DC converters, but one of the most common for stepping up voltage is called a "boost converter." Imagine a tiny energy storage tank (an inductor) that gets filled up with energy from the input source. Then, a switch quickly opens and closes, releasing that energy into another part of the circuit in a way that adds to the existing voltage. This process happens rapidly and repeatedly, effectively "boosting" the voltage.
These converters can range in size from tiny chips on a circuit board to larger, more powerful units designed for industrial applications. The efficiency of a DC-DC converter is a crucial factor. Ideally, you want a converter that converts as much of the input power as possible into output power, with minimal energy loss as heat. A good converter might be 80-95% efficient.
Beyond boost converters, there are also other types, such as buck-boost converters, which can both step up and step down voltage depending on the input conditions. The best choice for your needs depends on the specific application and the voltage ranges you're working with.

How To Increase And Decrease Dc Voltage (Step Up Down
Applications Galore
3. Powering the Modern World
So where might you encounter this voltage-boosting wizardry in the real world? Well, pretty much everywhere! Think about portable electronics. Your smartphone, laptop, and tablet all use DC-DC converters to efficiently manage power from their batteries and deliver the correct voltages to different components.
Solar power systems are another prime example. Solar panels typically produce a DC voltage that varies depending on sunlight. DC-DC converters are used to step up this voltage to a level suitable for charging batteries or feeding into the power grid. This ensures a consistent and usable power output, no matter how sunny it is.
Electric vehicles (EVs) also rely heavily on DC-DC converters. They're used to convert the high-voltage DC from the battery pack to lower voltages needed to power things like the lights, infotainment system, and other auxiliary equipment. They also enable efficient regenerative braking, capturing energy during deceleration and feeding it back into the battery.
Even in industrial settings, DC-DC converters play a vital role in powering various machinery and equipment. They provide a stable and regulated DC voltage, ensuring reliable operation and preventing damage to sensitive electronics. From small gadgets to large-scale systems, stepping up DC voltage is an essential technique for modern electronics.

Dc Step Up Converter Design
Understanding the Limitations and Considerations
4. It's Not Always a Free Ride
While stepping up DC voltage is a powerful tool, it's important to understand the limitations and trade-offs involved. As we mentioned earlier, you can't create energy from nothing. Increasing voltage usually means decreasing current, and there's always some energy loss due to the inefficiency of the converter.
Another consideration is the power rating of the DC-DC converter. You need to choose a converter that's capable of handling the amount of power you're dealing with. Overloading a converter can lead to overheating, damage, or even failure. It's always a good idea to choose a converter with a power rating that's comfortably above your expected load.
The ripple voltage on the output is another parameter to consider. Ripple voltage refers to the small fluctuations in the output voltage caused by the switching action of the converter. While some ripple is unavoidable, excessive ripple can interfere with the operation of sensitive electronic circuits. Using appropriate filtering techniques can minimize ripple voltage.
Finally, remember that DC-DC converters can generate electromagnetic interference (EMI). This is due to the rapid switching of current within the converter. Shielding and filtering techniques can be used to minimize EMI and prevent it from interfering with other electronic devices. Choosing a reputable converter from a reliable manufacturer can also help to ensure good EMI performance.
Variable Output Ac Voltage Power Supply
Troubleshooting Common Issues and FAQs
5. Dealing with Hiccups
Even with the best equipment, things can sometimes go wrong. If your DC-DC converter isn't working as expected, there are a few things you can check. First, make sure that the input voltage is within the specified range for the converter. Too low or too high of an input voltage can prevent the converter from operating correctly.
Next, check the output voltage with a multimeter. If the output voltage is significantly lower than expected, or if there's no output at all, there might be a problem with the converter itself. Check the connections for loose wires or bad solder joints. Also, check for any blown fuses or damaged components.
Overheating is another common issue. If the converter is getting excessively hot, it might be overloaded or there might be insufficient cooling. Make sure that the converter is properly heatsinked and that there's adequate airflow around it.
Sometimes, the problem might not be with the converter itself, but with the load it's powering. A short circuit or excessive current draw in the load can cause the converter to shut down or malfunction. Disconnect the load and test it separately to rule out any problems.
6. FAQ
Here are some frequently asked questions to help you further your understanding of DC voltage step-up:
Q: Can I use a DC-DC converter to step up the voltage from a single AA battery to 12V?A: Yes, absolutely! It might require a somewhat specialized converter designed for very low input voltages, and the output current will be limited, but it's definitely possible. The efficiency may not be fantastic at such a large step-up ratio, though.
Q: What happens if I connect a DC-DC converter backwards?A: Very bad things. Most converters have protection diodes, but reversing the polarity can still damage the converter, potentially causing it to fail or even explode (in a dramatic, albeit dangerous, fashion). Always double-check your polarity!
Q: How do I choose the right DC-DC converter for my project?A: Consider the input voltage range, the desired output voltage, the maximum output current, the efficiency, and the ripple voltage. Also, think about the size and form factor of the converter and whether it's suitable for your application. Read datasheets carefully!